Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Best Oral Product for Hair Loss?
HLCC HairScripts Complete is the most effective product that works for both Male and Female. It contains many ingredients that actually work to block DHT and in quantities that really matter. It also works to stimulate the scalp and bring dead follicles back to life.
What Is DHT and How it Damages the Hair?
DHT, Dihydrotestosterone, causes 95% of all hair loss. The interaction of DHT with androgen receptors in scalp skin and follicles appears to cause male and female pattern baldness. DHT miniaturizes hair follicles by shortening the anagen (growth) phase and/or lengthening the telogen (resting) phase. This causes the hair follicles to slowly shrink and die.
What Is Sebum and How Does it Affects Hair Loss?
The sebaceous oil building up causes sebum. Sebum collects in the hair follicle and hardens, causing a sebum plug that hinders hair growth. This compounded with existing weak hair causes reduction in hair growth.
Are Dryers, Tongs and Coloring OK to Use?
Many people believe that hair dryers, tongs, coloring, and over treating hair rank among the causes of hair thinning in women. This simply is not the case. Although they can cause hair to break off near the scalp, they are not long term causes of thinning hair in women.

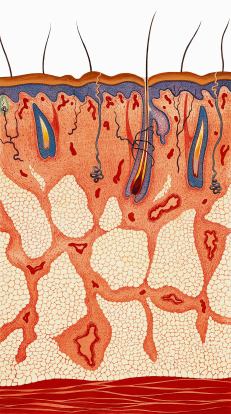
Why Are Hair Follicles?
Hair has two distinct structures - first, the follicle itself, which resides in the skin, and second, the shaft, which is what is visible above the scalp. The hair follicle is a tunnel-like segment of the epidermis that extends down into the dermis. The structure contains several layers that all have separate functions. At the base of the follicle is the papilla, which contains capillaries, or tiny blood vessels that nourish the cells. The living part of the hair is the very bottom part surrounding the papilla, called the bulb. The cells of the bulb divide every 23 to 72 hours, remarkably faster than any other cell in the body.
Two sheaths, an inner and outer sheath, surround the follicle. These structures protect and form the growing hair shaft. The inner sheath follows the hair shaft and ends below the opening of a sebaceous (oil) gland, and sometimes an apocrine (scent) gland. The outer sheath continues all the way up to the gland. A muscle called an erector pili muscle attaches below the gland to a fibrous layer around the outer sheath. When this muscle contracts, it causes the hair to stand up which also causes the sebaceous gland to secrete oil.
The sebaceous gland is vital because it produces sebum, which conditions the hair and skin. After puberty our body produces more sebum but as we age we begin to make less sebum. Women have far less sebum production than men do as they age.
What Are Hair Shafts?
The hair shaft is made of a hard protein called keratin and is made in three layers. This protein is actually dead, so the hair that you see is not a living structure. The inner layer is the medulla. The second layer is the cortex and the outer layer is the cuticle. The cortex makes up the majority of the hair shaft. The cuticle is a tightly formed structure made of shingle-like overlapping scales. It is both the cortex and the medulla that holds the hair's pigment, giving it its color.
What Is the Hair Growth Cycle?
Hair on the scalp grows about .3 to .4 mm/day or about 6 inches per year. Unlike other mammals, human hair growth and shedding is random and not seasonal or cyclical. At any given time, a random number of hairs will be in one of three stages of growth and shedding: anagen, catagen, and telogen.
What Is Anagen?
Anagen is the active phase of the hair. The cells in the root of the hair are dividing rapidly. During this phase the hair grows about 1 cm every 28 days. Scalp hair stays in this active phase of growth for two to six years.
What Is Catagen?
The catagen phase is a transitional stage and about 3% of all hairs are in this phase at any time. This phase lasts for about two to three weeks. Growth stops and the outer root sheath shrinks and attaches to the root of the hair. This is the formation of what is known as a club hair.
What Is Telogen?
Telogen is the resting phase and usually accounts for 6% to 8% of all hairs. This phase lasts for about 100 days for hairs on the scalp and longer for hairs on the eyebrow, eyelash, arm, and leg. Pulling out a hair in this phase will reveal a solid, hard, dry, white material at the root. About 25 to 100 telogen hairs are shed normally each day.
What Causes Hair to Grow?
The scalp is composed of 3 basic layers of skin: the epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous layer. Within these 3 layers there are blood vessels, nerves, muscles, glands, and hair (or keratin).
Hair growth is depended on oxygen and nutrients by the blood flow to promote cellular activity and new growth. When fewer nutrients reach the papilla, hair cells reproduce at a much slower rate. Slower cellular activity produces thin, poor quality hair. The sebaceous gland secretes oil in the follicle, coating the hair for smooth growth and creating healthy luster and sheen.
What is Hair Loss Treatment?
To understand hair loss treatments, you should first understand hair loss itself. There are many causes of hair loss. The primary cause is both male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness, affecting almost 50% of adult males and 25% of adult women. This cause of hair loss is directly related to changes in your hair's nutrition, levels of DHT and proper scalp hygiene.
DHT, or Dihydrotestosterone, causes 95% of all hair loss. The interaction of DHT with androgen receptors in scalp skin and follicles appears to cause male and female pattern baldness. DHT miniaturizes hair follicles by shortening the anagen (growth) phase and/or lengthening the telogen (resting) phase. This causes the hair follicles to slowly shrink and die. The sebaceous oil building up causes sebum. Sebum collects in the hair follicle and hardens, causing a sebum plug that hinders hair growth. This compounded with existing weak hair causes reduction in hair growth.
The good news is, even with thinning, fine hair, there is still life in the follicle. With the low-level laser technology (LLLT) and the proven HLCC regimen of proper hair nutrition, DHT blocking products and good scalp hygiene, you can repair thinning hair.
What Are the Causes of Hair Loss for Men?
The number 1 cause of male hair loss is Male Pattern Baldness and it is permanent. This is usually inherited, and the earlier in life it begins, the more extensive the baldness becomes.
Basically, hormones make hair follicles shrink, and when small enough, they cannot replace lost hairs. If your hair loss is characterized by a receding hairline and a bald patch on the top of the head, then you have male pattern baldness.
Is Male Baldness Preventable?
It is extremely important for you to know that male baldness is preventable if you start treating it when you first start noticing male hair loss. The longer you wait to treat it, the less hair you will be able to re-grow using the available male pattern baldness cures or treatments.
If you are experiencing excessive hair loss without common patterns, the causes are many and sometimes difficult to isolate.
What Are Other Common Causes of Male Baldness?
>> Poor Diet, especially lacking in protein and amino acids>> Surgery
>> Diabetes
>> Poor thyroid
>> Certain Medications, most notably blood thinners, those to treat gout, some antidepressants, and most forms of chemotherapy
>> Infections, usually fungal scalp infections
>> Diseases such as lupus
>> Psychological stressors: most commonly divorce, death, loss of job/income.
Many of the above-listed causes are temporary and/or treatable, and hair will return. In some instances, hair may return thinner then before.
What Are the Causes of Hair Loss for Women?
Women actually make up forty percent of American hair loss sufferers experiencing female pattern baldness and related emotional trauma. For women thinning hair is more traumatic than for men. We lose hair everyday, 100-150 strands actually, simply from brushing and manipulating. If hair is coming out in clumps, or you notice circular patches of balding spots, however, there is definitely a problem, and treatment will be based upon the specific cause of female hair loss. Diagnosis of the causes of hair thinning in women should be made by a physician.
What Are the Different Types of Hair Loss for Women?
Hair loss can be temporary or long lasting. The information in this section will help you identify the cause of your hair loss and ideally lead you and your doctors to the right treatments for your particular kind of hair loss, sooner, rather than later.
Alopecia is the medical term for excessive or abnormal hair loss. There are different kinds of Alopecia. Hair loss is always a symptom of something else that has gone wrong in your body such as hormone imbalance, disease, or some other condition. That condition may be as simple as having a gene that makes you susceptible to male or female pattern baldness or one of the forms of alopecia areata, or it may be as complex as a whole host of diseases may. Fortunately, hair loss may also be a symptom of a short-term event such as stress, pregnancy, and the taking of certain medications. Once the cause is determined, many times hairs will go back to their random pattern of growth and shedding, and the hair loss problem stops.
The Following Are the Most Common Causes of Women's Hair Loss:
Andogenetic AlopeciaAndrogenic alopecia in women is due to the action of androgens, male hormones that are typically present in only small amounts. Androgenic alopecia can be caused by a variety of factors tied to the actions of hormones, including, ovarian cysts, high androgen index birth control pills, pregnancy, and menopause. Just like in men the hormone DHT appears to be at least partially to blame for the miniaturization of hair follicles in women suffering with female pattern baldness. The majority of women with androgenic alopecia have diffuse thinning on all areas of the scalp. Some women may have a combination of two pattern types. Heredity plays a major factor in the disease. Hair loss through heredity thinning (Androgenic Alopecia) accounts for 95% of hair loss cases in women.
Telogen Effluvium
When your body goes through something traumatic like child birth, malnutrition, a severe infection, major surgery, or extreme stress, many of the 90 percent or so of the hair in the anagen (growing) phase or catagen (resting) phase can shift all at once into the shedding (telogen) phase. About 6 weeks to three month after the stressful event is usually when the phenomenon called telogen effluvium can begin. It is possible to lose handful of hair at time when in full-blown telogen effluvium. For most who sufferers complete remission is probable as long as severely stressful events can be avoided. For some women however, telogen effluvium is a mysterious chronic disorder and can persist for months or even years without any true understanding of any triggering factors or stressors.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium occurs when the hair follicle mitotic or metabolic activity is impaired. This hair loss is commonly associated with chemotherapy. Since chemotherapy targets your body's rapidly dividing cancer cells, your body's other rapidly dividing cells such as hair follicles in the growing (anagen) phase, are also greatly affected. Soon after chemotherapy begins approximately 90 percent or more of the hairs can fall out while still in the anagen phase. The characteristic finding in anagen effluvium is the tapered fracture of the hair shafts and causes the loss of hair.
Traction Alopecia
Anagen effluvium occurs when the hair follicle mitotic or metabolic activity is impaired. This hair loss is commonly associated with chemotherapy. Since chemotherapy targets your body's rapidly dividing cancer cells, your body's other rapidly dividing cells such as hair follicles in the growing (anagen) phase, are also greatly affected. Soon after chemotherapy begins approximately 90 percent or more of the hairs can fall out while still in the anagen phase. The characteristic finding in anagen effluvium is the tapered fracture of the hair shafts and causes the loss of hair.
The Following Are Other Causes of Female Hair Loss:
>> Diet: An unbalanced diet, Vitamin B12 deficiency or low iron levels>> Frequent Shampooing: Shampoos contain a lathering ingredient called surfactant, such as Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) and DEA
>> Oral Contraceptives are a common trigger of hair loss for many who use them
>> Menopause: Due to the change in hormones during this period, hair loss can escalate, and, unfortunately, this can be permanent.
>> Psychological/Physiological Stress: Temporary hair loss with pregnancies, major surgery, or a major life event, such as a death or divorce
>> Alopecia Areata: This is an autoimmune condition characterized by circular patches of baldness. Basically, the body is attacking the hair follicles. Cortisone shots in the affected areas are used
>> Other Health Conditions: Thyroid problems, lupus, and diabetes can accelerate hair loss
What is Laser Hair Therapy?
Laser Hair Therapy (LHT) is a non-surgical, scientific approach in the cosmetic treatment of hair loss, thinning hair, and scalp problems. Although we offer Cosmetic laser therapy, several Medical devices have now cleared the US FDA. The LHT cosmetic treatments utilize a device containing 110-160 therapeutic soft low light level lasers. LHT functions on the scientific principle, as photo-bio-stimulation; laser light stimulates cell metabolism and helps damaged cells to repair themselves. LHT has been tested for effectiveness and safety for over 30 years all around the world. This breakthrough technology has recently been featured on national newscasts across the country. Physicians are praising this new technology as an effective treatment of hair loss, when used in conjunction with proper scalp and hair hygiene products, such as HLCC Complete, the most potent natural DHT inhibitor and 5% Minoxidil w/ 5% Saw Palmetto.
How Lasers Came to be a Standard in Hair Loss Therapy?
The Laser was first used in Eastern Europe about 25 year ago to speed up the healing process of diseased individuals. Since the late 1700s, scientific studies have shown that sunlight- or the lack of it - definitely affects our body's biochemistry. Light also affects our hair, including how fast it grows. We have all experienced how our hair grows quicker during the summer, and this increased growth is due to improved blood supply to the hair follicles stimulated by the red light in sunlight.
How Lasers Repair Damaged Hair?
A laser produces light measured at a wavelength of nanometers typical between 638.2 nM and 670 nM--a pure wave-length at the peak of red light in the visible light spectrum. Laser Hair Therapy light provides the essential boost of pure red light at precisely the right frequency to revitalize and repair hair, yet it utilizes a soft laser that uses less energy than a 40-watt light bulb.
Although lasers vary in the strength of each diode, generally the more lasers diodes a person is sitting under during each laser treatment will provide better results.